몽고디비 공식사이트 : https://www.mongodb.com/
The most popular database for modern apps
We're the creators of MongoDB, the most popular database for modern apps, and MongoDB Atlas, the global cloud database on AWS, Azure, and GCP. Easily organize, use, and enrich data — in real time, anywhere.
www.mongodb.com
다운로드 : https://www.mongodb.com/download-center/community
MongoDB Download Center
Select the server you would like to run: MongoDB Enterprise ServerADVANCED FEATURES. PERFORMANCE GRADE. MongoDB offers both an Enterprise and Community version of its powerful non-relational database. MongoDB Enterprise is available as part of the MongoDB
www.mongodb.com
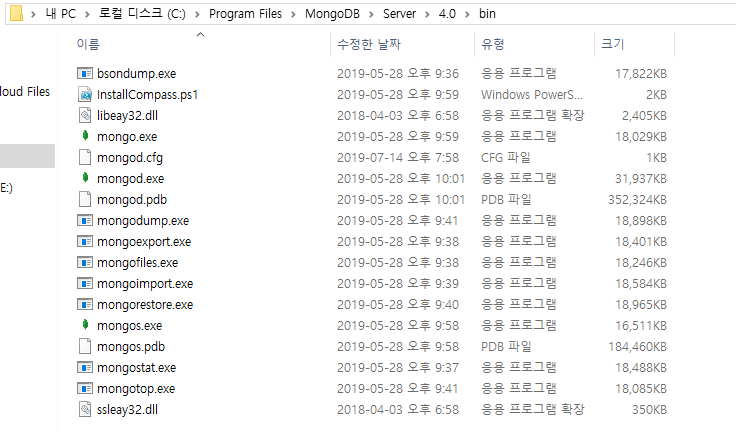
윈도우10 기준 mongoDB 환경설정 추가하기
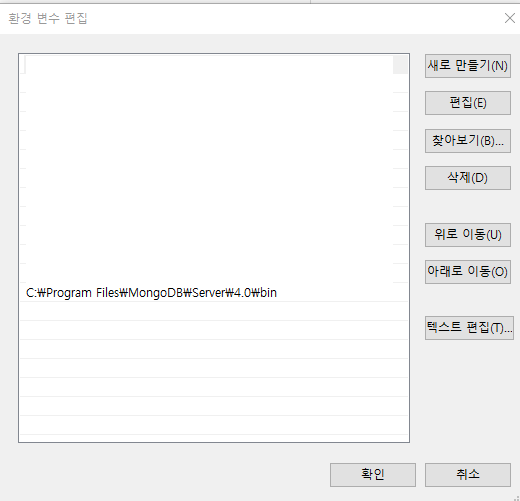
윈도우 키 + R => sysdm.cpl 입력 => 고급 => 환경변수 => 시스템 변수 리스트중에 Path 더블클릭 => 새로만들기 => 버전에 맞는 주소 입력 => 적용(확인)
적용되는지 확인하기)
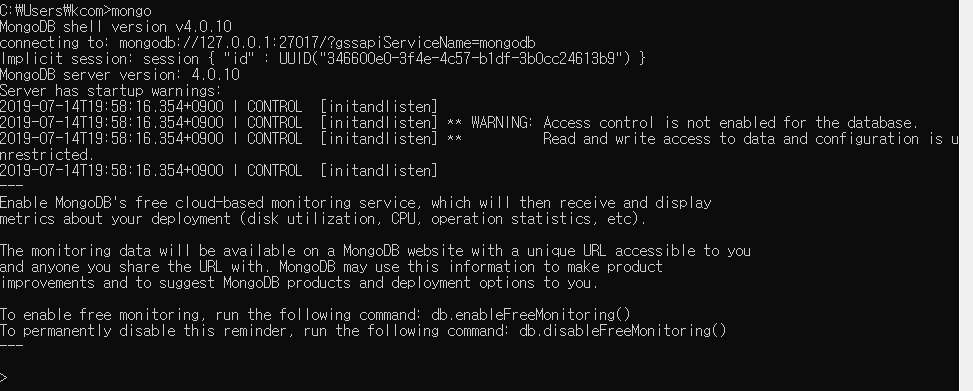
윈도우 키 + R => cmd 입력 => mongo
Mongoose : https://www.npmjs.com/package/mongoose
mongoose
Mongoose MongoDB ODM
www.npmjs.com
docs : https://mongoosejs.com/docs/
Mongoose v5.6.4: Getting Started
Getting Started First be sure you have MongoDB and Node.js installed. Next install Mongoose from the command line using npm: $ npm install mongoose Now say we like fuzzy kittens and want to record every kitten we ever meet in MongoDB. The first thing we ne
mongoosejs.com
npx create-react-app mongodb-ex01
yarn add mongoose dotenv
yarn add koa koa-router koa-bodyparser nodemon cross-env
yarn add joi dotenv : 환경변수들을 파일에 넣고 사용할 수 있게 하는 개발도구
mongoose : Node.js환경에서 사용하는 MongoDB 기반 ODM(Object Data Modeling) 라이브러리
package.json
"scripts": {
"start": "cross-env NODE_PATH=src node src react-scripts start",
"start:dev": "cross-env NODE_PATH=src node src react-scripts start nodemon --watch src/ src/index.js ",
"build": "cross-env NODE_PATH=src node src react-scripts build",
"test": "cross-env NODE_PATH=src node src react-scripts test",
"eject": "cross-env NODE_PATH=src node src react-scripts eject"
},윈도우인경우 cross-env 설치후 붙여넣습니다. 타OS(맥, 리눅스)는 구글검색을 하시길 바랍니다.
NODE_PATH = src node src 를 붙여주면 src로 주소가 패치된다.
.env
PORT = 4000
MONGO_URI = mongodb://localhost/blog
src/index.js
require('dotenv').config();
const Koa = require('koa');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const app = new Koa();
const {
PORT: port = 4000, // 값이 존재하지 않는다면 4000을 기본값으로 사용
MONGO_URI: mongoURI
} = process.env;
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise; // Node의 Promise를 사용하도록 설정
mongoose.connect(mongoURI).then(() => {
console.log('connected to mongodb');
}).catch((e) => {
console.error(e);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log('listening to port', port);
});
node src 입력후
http://localhost:4000/ 입력하기 아래와같이 콘솔에 출력되면 mongoose를 사용할 준비완료
listening to port 4000
connected to mongodb
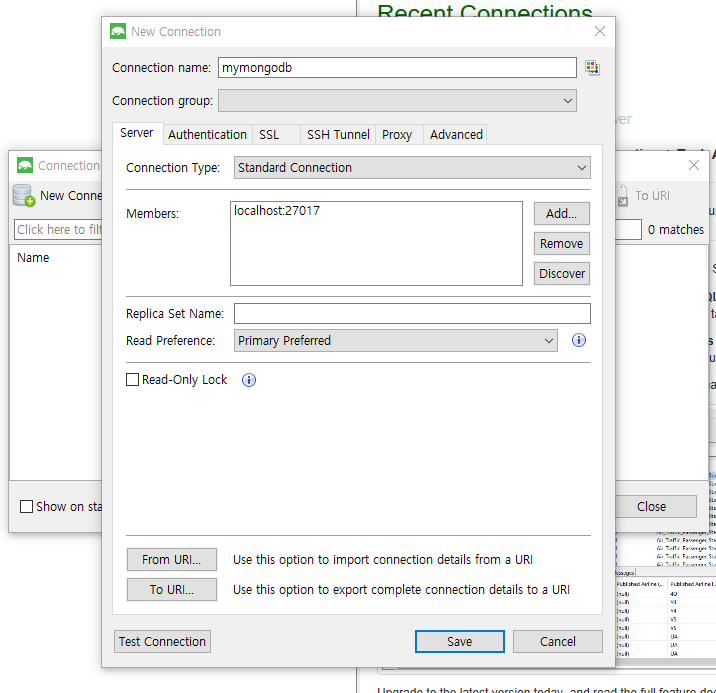
Robo 3T 사이트 : https://robomongo.org/download
Robomongo
The latest version Robomongo is now Robo 3T Robo 3T 1.3 brings you support for MongoDB 4.0 and SCRAM-SHA-256, an upgraded mongo shell, support for importing from MongoDB SRV connection strings, among many other fixes and improvements. Download Robo 3T
robomongo.org
src/models/post.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const { Schema } = mongoose;
// 스키마
const Post = new Schema({
title: String,
body: String,
tags: [String], // 문자열의 배열
publishedDate: {
type: Date,
default: new Date() // 현재 날짜를 기본값으로 지정
}
});
// mongoose.model(스키마 이름, 스키마 객체)
// 데이터베이스에는 스키마 이름뒤에 복수 s를 붙여 생성된다. ex) Post -> Posts
// 컨벤션을 따르지 않는다면 mongoose.model('Post', Post, 'custom_name'); 3번째 매개변수에 적으면된다.
module.exports = mongoose.model('Post', Post);
jsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions" : {
"baseUrl" : "./src"
}
}인텔리센스를 위한 패치
src/index.js
require('dotenv').config();
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const api = require('./api');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
const {
PORT: port = 4000, // 값이 존재하지 않는다면 4000을 기본값으로 사용
MONGO_URI: mongoURI
} = process.env;
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise; // Node의 Promise를 사용하도록 설정
mongoose.connect(mongoURI,{ useNewUrlParser: true }).then(() => {
console.log('connected to mongodb');
}).catch((e) => {
console.error(e);
});
// 라우터 설정
router.use('/api', api.routes()); // api 라우트 적용
// 라우터 적용 전에 bodyParser 적용
app.use(bodyParser());
// app 인스턴스에 라우터 적용
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log('listening to port', port);
});
src/api/index.js
const Router = require('koa-router');
const posts = require('./posts');
const api = new Router();
api.use('/posts', posts.routes());
// 라우터를 내보냅니다.
module.exports = api;
src/api/posts/index.js
const Router = require('koa-router');
const postsCtrl = require('./posts.ctrl');
const posts = new Router();
posts.get('/', postsCtrl.list);
posts.post('/', postsCtrl.write);
posts.get('/:id', postsCtrl.checkObjectId, postsCtrl.read);
posts.delete('/:id', postsCtrl.checkObjectId, postsCtrl.remove);
posts.patch('/:id', postsCtrl.checkObjectId, postsCtrl.update);
module.exports = posts;
src/api/posts/posts.ctrl.js
const Post = require('models/post');
const Joi = require('joi');
const { ObjectId } = require('mongoose').Types;
// ObjectId 검증
// src/api/posts/index.js 에서 checkObjectId를 활용한다.
exports.checkObjectId = (ctx, next) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
// 검증 실패
if (!ObjectId.isValid(id)) {
ctx.status = 400; // 400 Bad Request
return null;
}
return next(); // next를 리턴해주어야 ctx.body가 제대로 설정됩니다.
};
/*
POST /api/posts
{ title, body, tags }
*/
/*
Request Body 검증)
포스트를 작성할 떄 서버는 title, body, tags 값을 모두 전달받는다.
클라이언트가 값을 빼먹었을 때는 400 오류가 발생해야 한다.
지금은 따로 처리하지 않았기 때문에, 요청 내용을 비운상태에서
write API를 실행해도 요청이 성공하여 비어 있는 포스트가 등록이 된다.
객체를 검증하려고 각 값을 if문으로 검증하는 방법도 있지만, 이를 수월하게 하는 라이브러리인
Joi를 설치하여 사용한다.
*/
// await 를 사용할려면 async 를 붙여줘야한다.
exports.write = async (ctx) => {
// 객체가 지닌 값들을 검증합니다.
const schema = Joi.object().keys({
title: Joi.string().required(), // 뒤에 required를 붙여주면 필수 항목이라는 의미
body: Joi.string().required(),
tags: Joi.array().items(Joi.string()).required() // 문자열 배열
});
// 첫 번째 파라미터는 검증할 객체, 두 번째는 스키마
const result = Joi.validate(ctx.request.body, schema);
// 오류 발생 시 오류 내용 응답
if (result.error) {
ctx.status = 400;
ctx.body = result.error;
return;
}
const { title, body, tags } = ctx.request.body;
// 새 Post 인스턴스를 생성합니다.
const post = new Post({
title, body, tags
});
try {
await post.save(); // 데이터베이스에 등록합니다.
ctx.body = post; // 저장된 결과를 반환합니다.
} catch (e) {
// 데이터베이스의 오류 발생
ctx.throw(e, 500);
}
};
/*
GET /api/posts
*/
exports.list = async (ctx) => {
// page가 주어지지 않았다면 1로 간주
// query는 문자열 형태로 받아오므로 숫자로 변환
const page = parseInt(ctx.query.page || 1, 10);
// 잘못된 페이지가 주어졌다면 오류
if (page < 1) {
ctx.status = 400;
return;
}
// .sort({ _id: -1 }) -> 역순
// limit() -> 갯수 제한
// skip -> 페이지기능 관련 코드 ex) posts?page=2
// └ skip 는 넘기다라는 뜻, 파라미터로 10을 넣어주면 첫 열개를 제외하고, 그 다음 데이터를 불러온다.
// lean -> 내용 길이 제한 -> const limitBodyLength 관련코드 -> JSON형식으로 반환
// └ 쿼리를 할 때 lean 함수를 사용하여 처음부터 JSON 형태로 조회하는 방법
// exec 붙여야만 서버에 쿼리를 요청
try {
const posts = await Post.find()
.sort({ _id: -1 })
.limit(10)
.skip((page - 1) * 10)
.lean()
.exec();
// Documents 총갯수 구하기
const postCount = await Post.countDocuments().exec();
// 200자 제한
const limitBodyLength = post => ({
...post,
body: post.body.length < 200 ? post.body : `${post.body.slice(0, 200)}...`
});
ctx.body = posts.map(limitBodyLength);
// 마지막 페이지 알려주기
// ctx.set은 response header를 설정해줍니다.
ctx.set('Last-Page', Math.ceil(postCount / 10));
} catch (e) {
ctx.throw(500, e);
}
};
/*
GET /api/posts/:id
*/
exports.read = async (ctx) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
try {
// findById : 특정 id를 가진 데이터를 조회
const post = await Post.findById(id).exec();
// 포스트가 존재하지 않음
if (!post) {
ctx.status = 404;
return;
}
ctx.body = post;
} catch (e) {
ctx.throw(e, 500);
}
};
/*
DELETE /api/posts/:id
*/
/*
remove : 특정 조건을 만족하는 데이터들을 모두 지운다.
findByIdAndRemove : id를 찾아서 지운다.
findOneAndRemove : 특정 조건을 만족하는 데이터 하나를 찾아서 제거한다
*/
exports.remove = async (ctx) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
try {
await Post.findByIdAndRemove(id).exec();
ctx.status = 204;
} catch (e) {
ctx.throw(e, 500);
}
};
/*
PATCH /api/posts/:id
{ title, body, tags }
*/
exports.update = async (ctx) => {
const { id } = ctx.params;
try {
// findByIdAndUpdate : 첫번쨰 파라미터는 id고, 두 번째 파라미터는 업데이트 내용이며, 세번째 파라미터는 업데이트의 설정 객체
const post = await Post.findByIdAndUpdate(id, ctx.request.body, {
new: true
// 이 값을 설정해 주어야 업데이트된 객체를 반환합니다.
// 설정하지 않으면 업데이트되기 전의 객체를 반환합니다.
}).exec();
// 포스트가 존재하지 않을 시
if (!post) {
ctx.status = 404;
return;
}
ctx.body = post;
} catch (e) {
ctx.throw(e, 500);
}
};
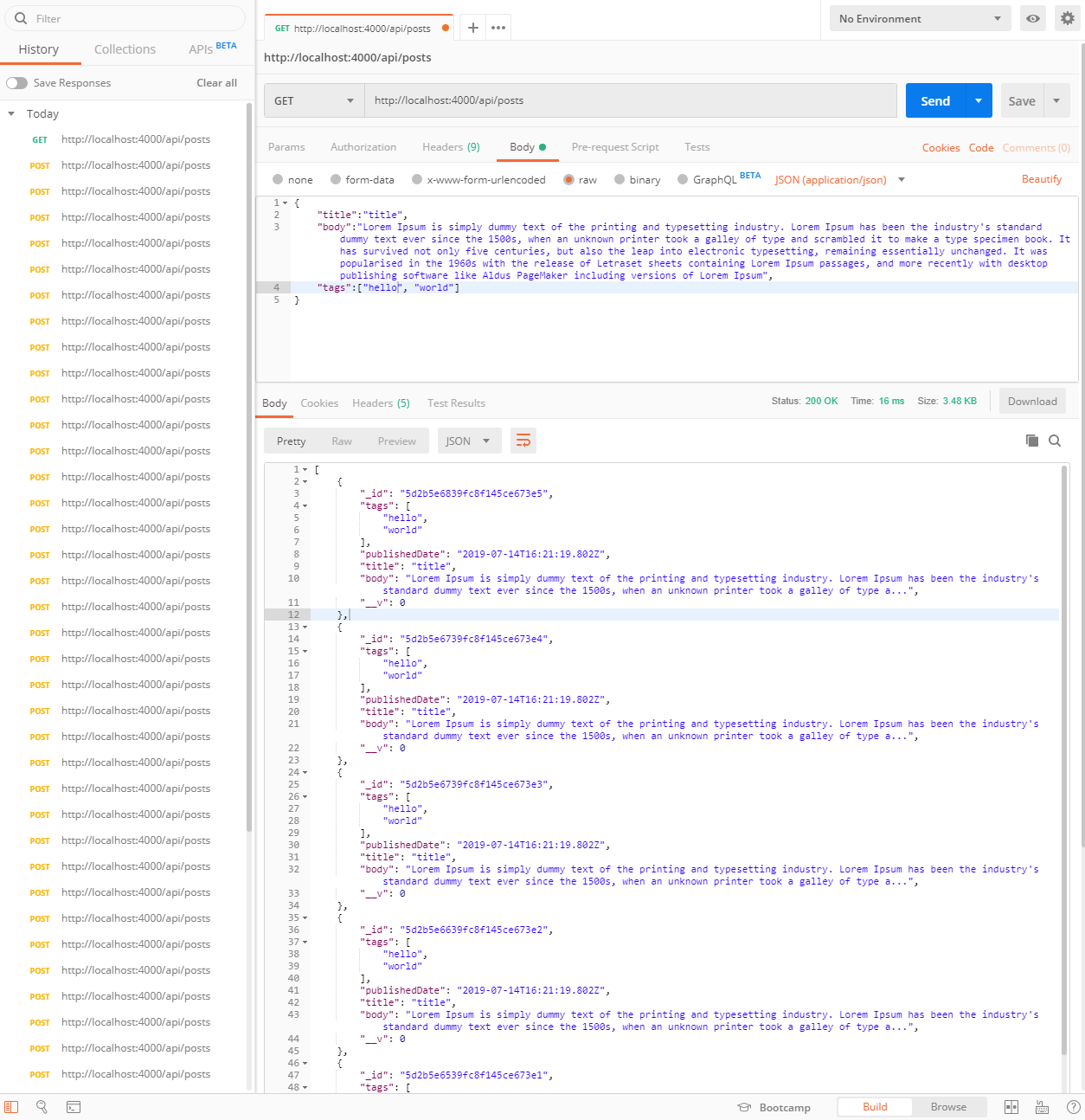
결과)
'WEB > REACT' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 17. [토이프로젝트 따라하기] 블로그-2 (0) | 2019.07.16 |
|---|---|
| 16. [토이프로젝트 따라하기] 블로그-1 (0) | 2019.07.15 |
| 14. Koa 프레임워크 (0) | 2019.07.14 |
| 13. 코드 스플리팅 (0) | 2019.07.13 |
| 12. react-router로 SPA (0) | 2019.07.12 |
